In an electrical circuit, if one input terminal were disconnected or shorted, half of the electrical pressure, or voltage, would be lost.
This would reduce the input level to the device by a 2-to-1 voltage ratio, or 6 dB.
When properly driven from a balanced signal source, the differential input provides a great deal of noise immunity for the sound system.
Also of importance in the mechanical and electrical circuits is proper balancing of the impedances of each input terminal (electrical) or pedal (mechanical).
We would not want to have to pedal harder with one foot than the other, so a balanced opposition to the force of the rider’s foot is desired. In the electrical example, if one input terminal has a higher input impedance than the other, then an imbalance results which will reduce the effectiveness of the input in rejecting unwanted (common-mode) input signals.
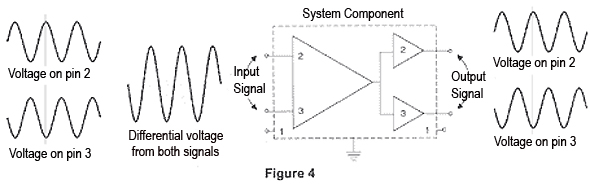
Of course, all analogies fall short at some point, but hopefully this one has helped in gaining understanding of balanced differential inputs.
