Before even attempting on the simulation software, the sound system designer must be able to lay down the desired sound system performance characteristics such as targeted maximum SPL (sound pressure level), maximum allowable SPL spread between the front and rear seats and frequency response target.
A good technical knowledge of the applications of loudspeakers including the characteristics and limitations of point source loudspeakers and line arrays is also required.
Since no sound system is perfect, trade-offs between various performance parameters are inevitable and hence experience and strong technical background are required to perform these trade-offs.
It is advantageous for the seating arrangement to be planned together with the sound system design since there will always be non-optimal sound quality areas. This may include areas which have “phasing” challenges for example locations directly in between similar loudspeaker clusters.
For this case, it would be best to have aisles instead of seats for such locations.
In like manner, when video projection screens are being utilized, both seating arrangement and the loudspeaker positions have to be considered together. There should be acceptable view angles from the seats to the projection screens. The positions of the loudspeakers are carefully selected to avoid excessive localization errors between the visual source and sound source.
For best performance, it is essential to consider the sound system, video projection system and seat arrangements altogether as a system during the design stage to enable appropriate trade-offs to be made up front.
12. Sound Equipment Quality
During the design stage, the quality of the sound equipment must also be taken in account. Since the failure of a single piece of equipment may very well fail the entire sound system, the reliability of each piece of equipment and the quality of the service support must be considered.
As for the sound quality aspect, reputable pro-audio sound equipment manufacturers are usually able to design pretty decent sounding electronic equipment such as sound mixers, loudspeaker processors and power amplifiers. These days, the quality of the electronics are usually quite decent especially with the use of high sampling rate and high resolution analog-digital converters and well established digital processing for the loudspeaker processors.
As for power amplifiers, the electronic designs to achieve good sound have been well established over the years. The main challenge for accurate sound reproduction lies in the conversion of electrical energy to sound energy. As such, the main distinction of the overall sound quality among various manufacturers is usually highly dependent on the sound quality of the loudspeaker system.
Therefore, there is an obvious desire to keep up to date in the pro audio world to constantly look out for reputable manufacturers who are able to design nice sounding loudspeakers and the associated electronics such loudspeaker processors and power amplifiers which are sometimes also built into the loudspeakers.
13. Sound System Optimization
Having a good sound system design with good quality sound equipment is not the end point. The next stage involves optimizing the sound system. This typically involves adjusting the parameters of the loudspeaker processors for optimum performance. These parameters are usually related to equalization settings, loudspeaker cross-over parameters and delay settings.
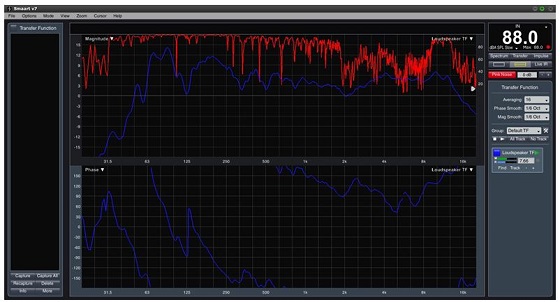
Appropriate objective measurement technique such as transfer function measurement based on dual-channel FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) or TDS (Time Delay Spectrometry) is often used as a starting point to aid in sound system optimization with subjective auditory confirmation that the settings chosen is acceptable.
The measurement also requires supporting acoustical measurement equipment including measurement microphone, sound card and computer software. A screen capture of such a measurement tool is shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: A screen capture of a dual channel FFT acoustic software (SmaartLive 7) that performs the frequency response measurement of a loudspeaker.